|
Boeing Satellite Systems,
(BSS), a major supplier of sophisticated, state-of-the-art
radio frequency (RF), microwave, and antenna subsystems,
has been part of the Milstar satellite team since 1982.
Milstar is the tactical and
strategic multiservice satellite system designed to
provide survivable communications for U.S. forces
worldwide. The program is managed by the U.S. Air Force
Space and Missile Center.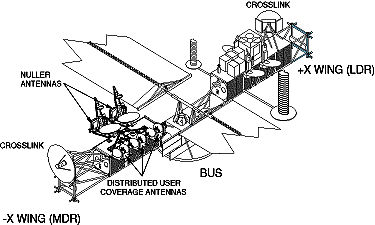
The Milstar I satellites
carry a secure, robust low-data-rate (LDR) communications
payload, and a crosslink payload that allows the
satellites to communicate globally without using a ground
station. The Milstar II satellites extend the
communications capabilities to higher data rates by adding
a medium-data-rate (MDR) payload. The Milstar I and II
satellites are fully interoperable for LDR communications
and crosslinks.
Boeing has the prime
responsibility for supplying the MDR and crosslink
payloads to prime contractor Lockheed Martin Missiles and
Space Company. BSS subcontracts with TRW Space and
Electronics Group for the MDR antennas and digital
subsystem, and provides portions of the LDR payload under
subcontract to TRW.
Milstar MDR meets the needs
of multiple users by supporting the connectivity of
tactical and conventional forces. Milstar LDR supports
strategic and tactical requirements for high anti-jam and
nuclear scintillation protection. Using the crosslinks,
the constellation supports multiple users simultaneously
without reliance upon physically vulnerable nodes.
Milstar's space assets provide a "communications
switch in the sky."
Communications features of
the MDR and LDR payloads are compared in the table below.
| |
MDR |
LDR |
| Data
rate |
4.8
kbps - 1544 kbps |
75
bps - 2400 bps |
No.
communications
channels |
32 |
192 |
| No.
users/channel |
1-70 |
1-4 |
| Coverages |
8
high-gain narrow
spot beams |
2
narrow spot beams
1 wide spot beam
1 earth coverage antenna
1 UHF transmit antenna
1 UHF receive antenna
5 earth coverage uplink
agile beams
1 earth coverage downlink
agile beam |
| Anti-jam |
Waveform
Nuller - active
Transmission security |
Waveform
Transmission security |
The Milstar system provides
uplink communications at extremely high frequency (EHF),
44 GHz, and ultrahigh frequency (UHF), 300 MHz, and
downlink communications at super-high frequency (SHF), 20
GHz, and UHF, 250 MHz. The crosslinks operate in the 60
GHz region. Survivability and endurability requirements
are satisfied by anti-jam, hardening and system autonomy
features.
MDR PAYLOAD
The MDR payload provides
secure, jam-resistant communications services through
unique onboard signal and data processing capabilities. It
sends real-time voice, video and data to military
personnel in the field at rates up to 1.5 Mbps. The
payload uses a 32-channel EHF uplink and an SHF downlink.
The MDR payload dynamically
sorts incoming data and routes them to the proper
downlinks to establish networks and provide bandwidth on
demand. If necessary it passes the data on to another
satellite via crosslink.
As the supplier of the MDR
payload, BSS integrates antennas and electronic units onto
the MDR structure, called the -X (minus X) wing, provided
by Lockheed Martin. (see satellite diagram above)
Antennas
The MDR antenna coverage
subsystem consists of eight narrow spot beam antennas
provided by TRW: two narrow spot beams with nulling
capabilities (nuller antennas) and six distributed user
coverage antennas (DUCAs), each supporting two-way
communications.
In contrast to commercial
communications satellites, whose beams can cover entire
continents, Milstar's beams are very narrow, providing
less opportunity for enemy detection and penetration. The
nuller antennas resist jamming from within their
respective coverage areas by changing their gain patterns
when a jamming signal is detected. The DUCAs provide high
gain/low sidelobes for distributed users.
Radio Frequency Subsystem
(RFSS)
The RF subsystem includes
the processing and receiving components and the downlink
group. The processing and receive group performs the
following four payload functions:
- amplifies, dehops, and
downconverts the EHF waveform to the first
intermediate frequency (IF) via the low-noise
amplifier/downconverter;
- receives, amplifies,
downconverts, and switches the first IF to the second
IF for input to one of four demodulator groups of
eight channels each;
- employs a differential
phase shift key (DPSK) to modulate and upconvert onto
a hopped SHF carrier for input to the downlink group;
and
- generates and
distributes the hopping and fixed local oscillators
for the antenna coverage subsystem, digital subsystem
and RFSS.
The downlink group
amplifies, filters and switches, on a hop-by-hop basis,
the SHF waveform to any of the eight antennas. The SHF
amplifiers are triple-redundant traveling wave tube
amplifiers. Switching capability is provided by a high
speed/high power beam select switch.
Digital Subsystem
The digital subsystem
consists of the demodulator, the data router and control
processor, the crosslink processor and the Milstar
Advanced Processor. The subsystem has five major
functions:
- demodulate uplink
baseband data;
- provide the switching
and routing of the incoming uplink and crosslink
baseband data to the downlink and crosslink
destinations;
- provide the uplink and
downlink acquisition and tracking control protocols;
- provide on-board
resource allocation enabling dynamic user
connectivity; and
- provide the interface to
the spacecraft
Together the MDR payload
weighs about 1100 pounds and uses 860 watts.
CROSSLINK PAYLOAD
Like a handshake in space,
crosslinks provide rapid, ultra-secure communications by
enabling the satellites to pass signals to one another
worldwide while requiring only one ground station on
friendly soil. The crosslink payload provides V-band (60
GHz) data communications between Milstar satellites for
both the MDR and LDR payloads. This includes modulation
and demodulation of the data, upconversion, amplification
for transmission and downconversion.
On Dec. 15, 1995, Milstar
was the world's first satellite constellation, government
or commercial, to employ crosslinks. A message was
uplinked from the national Military Command Center at Fort
Belvoir, Va., through the Milstar F-1 satellite. It was
crosslinked to the Milstar F-2 spacecraft, then downlinked
to commanders at Pacific Command at Camp H.M. Smith,
Hawaii, and U.S. Atlantic Command at Norfolk, Va.
The major crosslink payload
elements are as follows:
- Millimeter wave
assemblies - include the antenna group with
autotracking modulator, transmit and receive
downconverter and telemetry/command unit. There are
two assemblies, one on the -X wing and one on the +X
wing.
- I-Panel assembly -
includes receivers, acquisition unit and autotrack
unit.
Together this equipment
weighs approximately 800 pounds and uses 260 watts.
LDR PAYLOAD
The LDR payload offers
nearly 200 user channels and relays coded teletype and
voice messages at data rates of 75 to 2400 bits per
second.
Boeing Satellite Systems
provides five major elements for the LDR payload, as
follows:
- Time and frequency
reference subsystem -- includes time-of-day clock for
system timing and synchronization for spectrally pure
frequency generation, and for dehopping of EHF uplink
frequencies and hopping of SHF downlink frequencies.
- SHF subsystem transmit
equipment group -- provides downlink modulation and
power amplification at 20 GHz.
- Synthesizer select
switch -- provides connectivity between wideband
frequency synthesizers and EHF downconverters.
- EHF downconverters --
receive 44 GHz uplink, dehops it and downconverts to
an intermediate frequency.
- Antenna positioner
equipment includes beam steering mechanisms and
control electronics for three shared-aperture EHF/SHF
spot beam antennas.
Together these elements
weigh approximately 600 pounds and use 350 watts.
|